Soil structure &
its compositions
Soil composition is an important aspect of nutrient management. While soil minerals and organic matter hold and store nutrients, soil water is what readily provides nutrients for plant uptake. Soil air, too, plays an integral role since many of the microorganisms that live in the soil need air to undergo the biological processes that release additional nutrients into the soil.
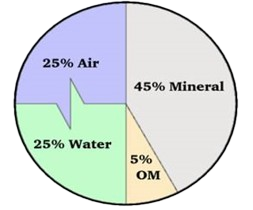
The basic components of soil are minerals, organic matter, water and air. The typical soil consists of approximately 45% mineral, 5% organic matter, 20-30% water, and 20-30% air. These percentages are only generalizations at best. In reality, the soil is very complex and dynamic. The composition of the soil can fluctuate on a daily basis, depending on numerous factors such as water supply, cultivation practices, and/or soil type.
Soil organic matter
Typically, the organic carbon content of dryland agricultural soils is between 0.7% and 4% , although SOC ( soil organic carbon) can be as low as 0.3% for desert soils and as high as 14% for intensive dairy soils. Most organic matter is located near the soil surface.
The solid phase of soil, which includes minerals and organic matter, are generally stable in nature. Yet, if organic matter is not properly managed, it may be depleted from the soil. The liquid and gas phases of the soil, which are water and air respectively, are the most dynamic properties of the soil. The relative amounts of water and air in the soil are constantly changing as the soil wets or dries.
Soil organic carbon can be maintained by application of siesto green bio capsules which contains trillions of beneficial microbes that will enhance the growth and multiplication of plant soil microbiome.As a result it will enhance plants nutrition efficiency, abiotic stress tolerance and crop quality and it plays a major role in soil aggregation process and stimulate microbial activity by improving soil structure and fertility .the bacteria present in the NPK capsule able to convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia as well as solubilization of phosphate and mobilization of potash which in turn is taken up and utilized by the plants.


