The Importance of
Soil pH in Agriculture
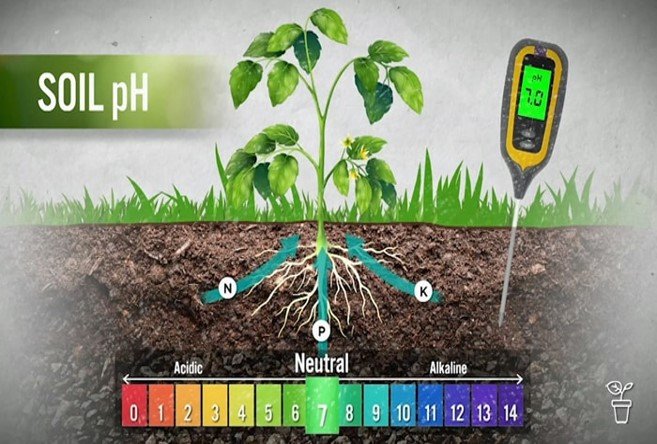
Soil pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity level of soil, measured on a scale of 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is alkaline.
In farming, soil pH is important because it influences nutrient availability, microbial activity, and overall soil health. Most plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soils, with a pH range of 6 to 7.5. When soil pH deviates from this range, it can affect plant growth and yield.
For example, acidic soils (pH below 6) can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. This can stunt plant growth and reduce crop yields.
On the other hand, alkaline soils (pH above 7.5) can cause micronutrient deficiencies and hinder nutrient uptake, leading to similar problems.
Humigrow Nano Benefits
Siesto green team has developed HUMIGROW NANO POWDER It contains mixture of humic substances & some natural Growth agent like amino acid.it is Water soluble. Humic acid acts as a buffer in the soil, helping to moderate and stabilize pH levels.
Here’s how it works:
- Acidic Soils: In acidic soils, Humigrow can help neutralize some of the acidity. It does this by having functional groups that can bind to hydrogen ions (H+), which are what make a soil acidic. By tying up these hydrogen ions, humic acid reduces their overall effect on the soil’s pH.
- Buffer Capacity: More importantly, humic acid improves the soil’s buffering capacity. This means the soil is better at resisting changes in pH, whether from natural processes like rain or from adding fertilizers. This buffering capacity is crucial for plant health, as many plants prefer a specific pH range for optimal growth.
- Indirect Effects: By improving overall soil health, humic acid can also indirectly influence pH. Healthy soil with a good organic matter content tends to be more resistant to pH fluctuations. Humic acid contributes to this by promoting beneficial soil microbes and improving soil structure.


